Center for Disease Control
Hispanic/Latino Americans and Type 2 Diabetes
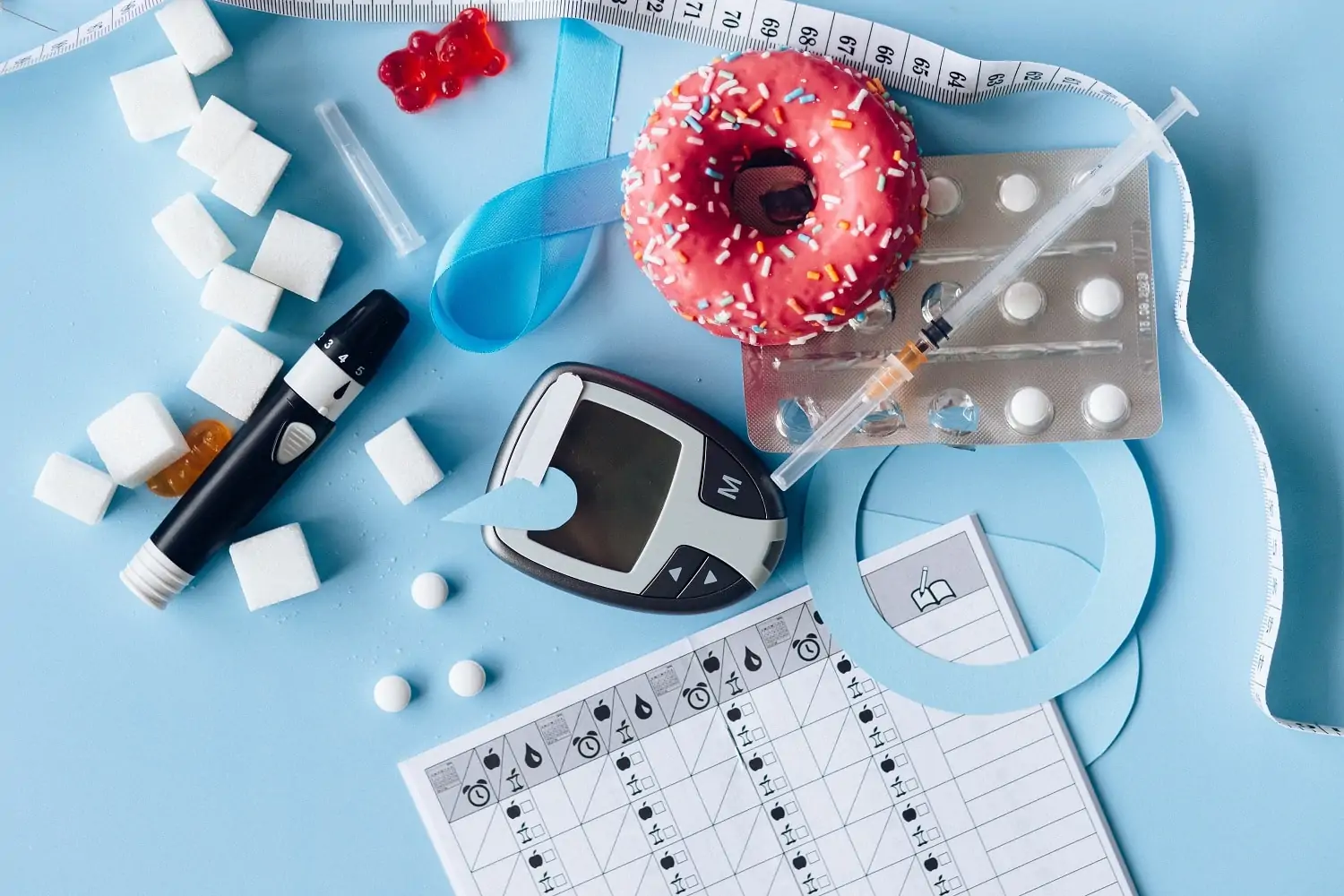

Diabetes is a serious condition that causes higher than normal blood sugar levels. Hispanic/Latino Americans are particularly vulnerable to developing type 2 diabetes with more than 50% higher chances of developing it in their lifetime.
Hispanic/Latino Americans and Type 2 Diabetes

What is Diabetes?

What is diabetes

What is Diabetes?

Facts About Diabetes
National Diabetes Prevention Program

Simple Steps to Preventing Diabetes

How to Prevent Diabetes

Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP)

Getting The Right Support From A CDC-Recognized Diabetes Prevention Program

Treatment & Care: Get the right care for you

Diabetes Medications

Insulin, Medicines, & Other Diabetes Treatments

Opciones para cocinar más saludable
Programa Nacional de Prevención de la Diabetes

Obteniendo El Mejor Apoyo De Un Programa De Prevención De Diabetes Reconocido Por CDC

De qué manera puede ayudarle un especialista en educación y cuidado de la diabetes

Recursos, Materiales en Español
Type 1 diabetes must be treated through a daily regimen of insulin therapy. The amount of insulin taken is dependent on:
The onset of type 1 diabetes is very quick. The following symptoms can occur sudden:
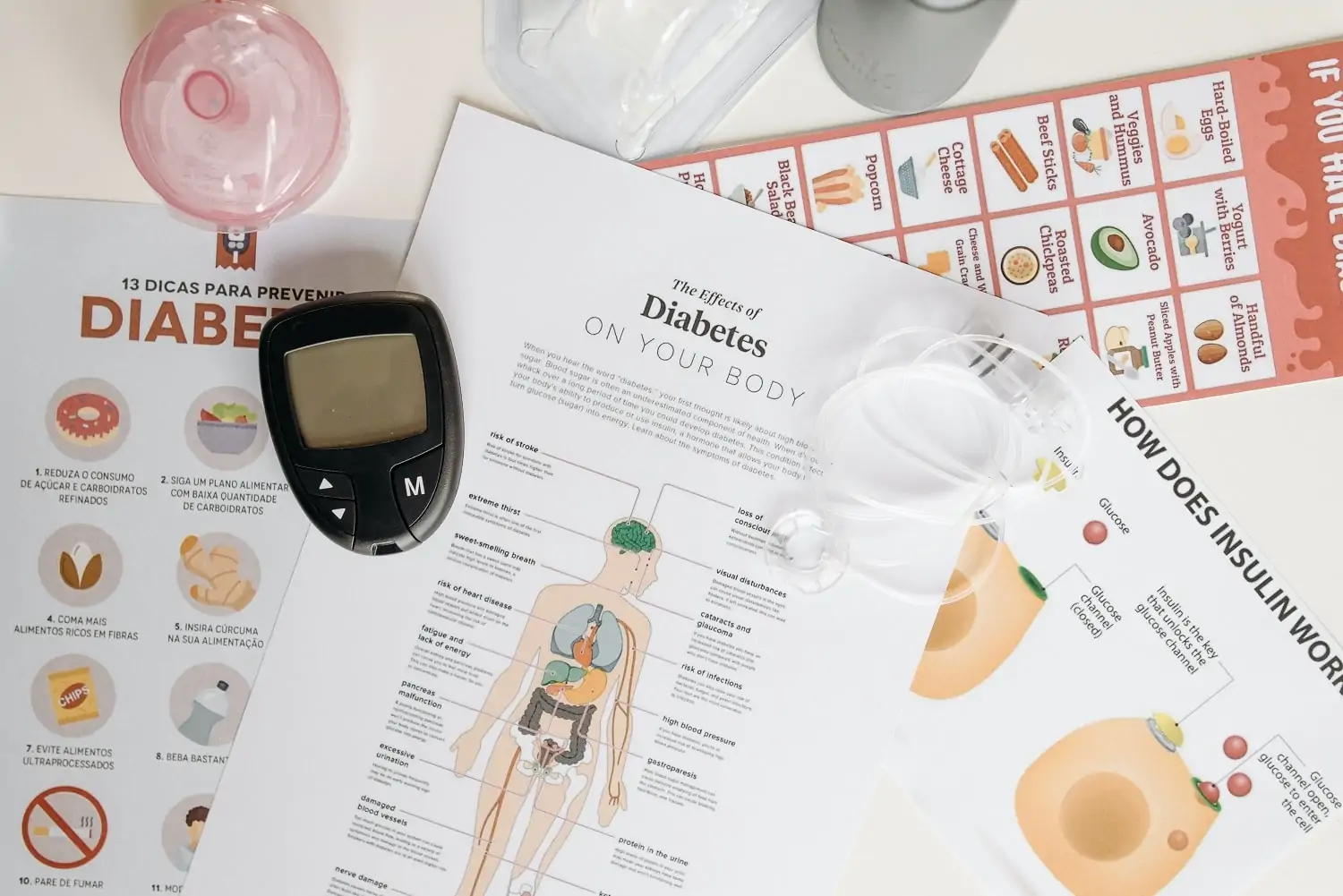

The warning signs of type 2 diabetes include:
These symptoms are often slower to present themselves and develop. It is important to talk to a doctor if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as they can often be mistaken for other conditions.
The main treatment for type 2 diabetes is improving the use of insulin by the body. This can include:
Some medications and in some cases, insulin, can act as a treatment for type 2 diabetes.
In order to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes can be made. These lifestyle changes include: