
Mpox Resources for Providers
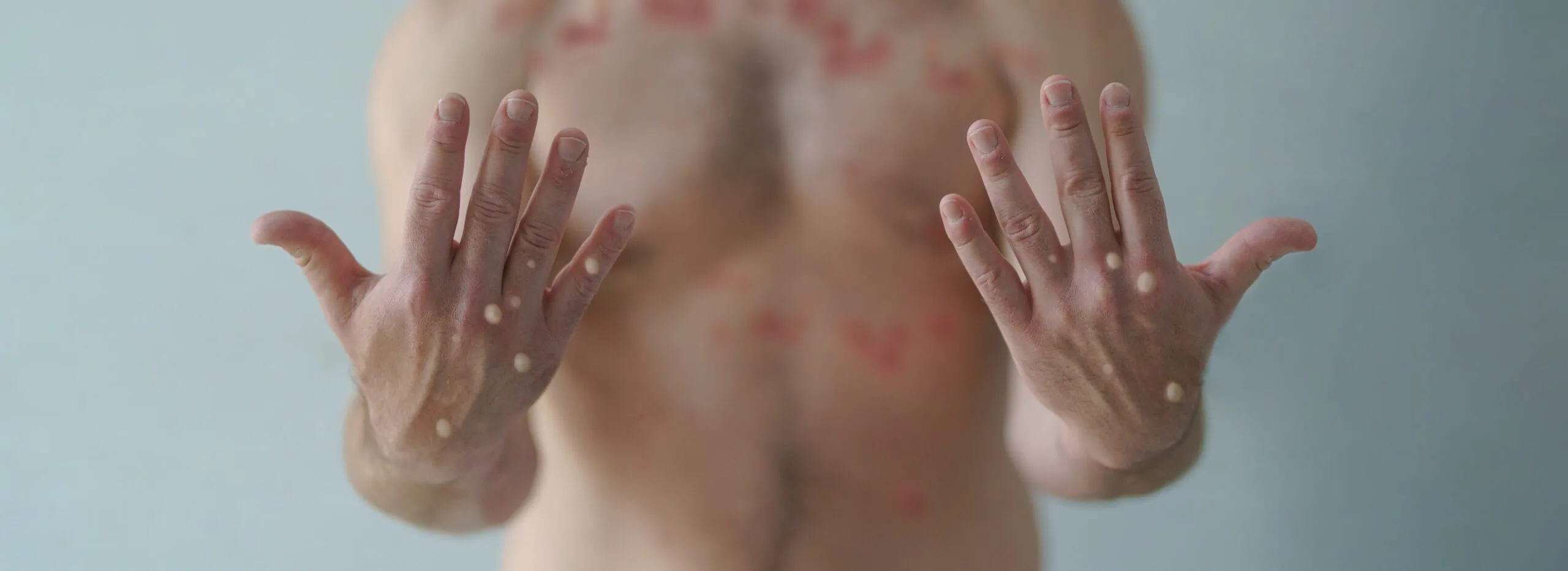
As a member of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s HIV PACT program, NHMA has developed this page to provide guidance to healthcare professionals treating cases of mpox (previously known as monkeypox). Mpox primarily presents as a rash that may be located on hands, feet, chest, face, or mouth or near the genitals, including penis, testicles, labia, and vagina, and anus, but may be accompanied by other symptoms.
Symptoms:
People with mpox often get a rash that may be located on hands, feet, chest, face, or mouth or near the genitals, including penis, testicles, labia, and vagina, and anus. The incubation period is 3-17 days. During this time, a person does not have symptoms and may feel fine.
The rash will go through several stages, including scabs, before healing.
The rash can initially look like pimples or blisters and may be painful or itchy.
Other symptoms of mpox can include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Exhaustion
- Muscle aches and backache
- Headache
- Respiratory symptoms (e.g., sore throat, nasal congestion, or cough)
You may experience all or only a few symptoms.
- Sometimes, people have flu-like symptoms before the rash.
- Some people get a rash first, followed by other symptoms.
- Others only experience a rash.

How long do mpox symptoms last?
Mpox symptoms usually start within 3 weeks of exposure to the virus. If someone has flu-like symptoms, they will usually develop a rash 1-4 days later.
A person with mpox can spread it to others from the time symptoms start until the rash has fully healed and a fresh layer of skin has formed. Some people have been found to have infection but no symptoms. CDC will continue to monitor for new or changing information about transmission.


